Microsoft® Active Directory Domain Services Support

Over View of Directory Services:
A directory service provides the ability to store information about network devices and services, and the people who use them, in a central location with a distributed environment. A directory service also implements the services that make this information available to users, computers and application. Therefore, a directory service is both a directory (the store of this information) and a set of services that provide the means to securely add, modify, delete, and locate data in the directory store.
Active Directory Domain Services Overview:
Active Directory Domain Service is the network focused directory service included in the windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 and windows server 2008, 2008 R2, and Windows server 2012 & 2012 R2 family of operating systems. AD DS delivers an extensible and scalable service that provides network authentication, administration and management of directory services to an organization running windows based network infrastructure.
Below figures illustrates the benefit of AD DS and how it acts as the local point of windows server 2008 R2 and 2012 R2 network, demonstrating how it can be used to manage identities and broker relationship between distributed sources.
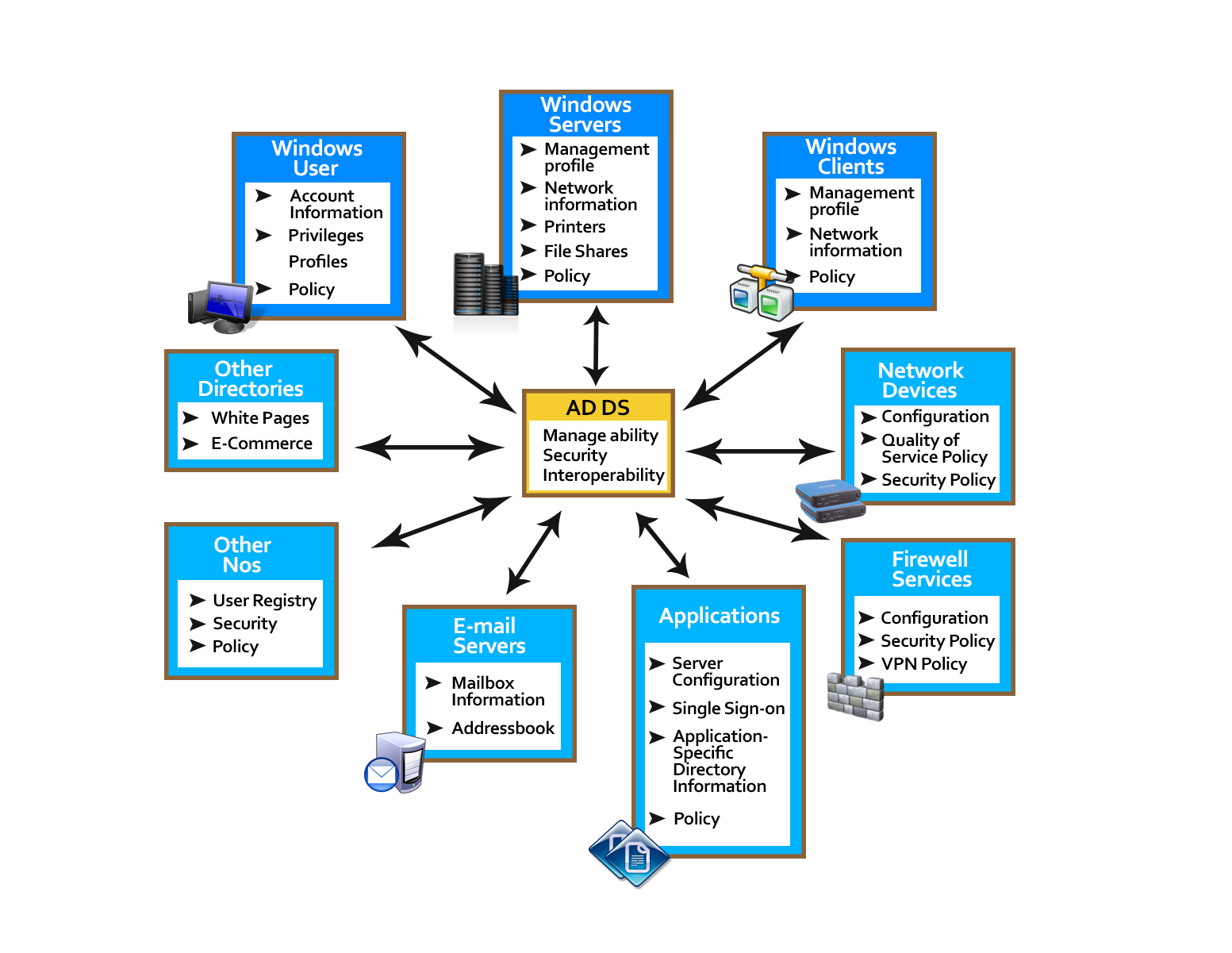
Figure: AD DS on a Windows Server 2012 R2 Network.
AD DS Provides:
! A Central location for network administration and the delegation of administrative authority
AD DS acts as a repository for objects representing all network users, devices, and resources, and provides the ability to group objects for ease of management and the application of security and group policy. Group policy refers to applying policy (Configuration Settings) to group of computers and/or users in Active Directory Domain Service.
! Information Security and Single sign-on for user’s access to local network resources
Tight integration with security eliminates costly tracking of accounts for authentication and authorization between systems. A single user names and password (or smartcard) combination can identify each network user, and this identity follows the user throughout the local network.
! Scalability
Active Directory Domain Service can be designed and implemented in numerous configurations to achieve scalability from a single site with a small number of users, to a highly complex large-scale site to meet any current and future network authentication requirements.
! Easy and flexible searching of the Active Directory
Users and administrators can use Windows xp, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 desktop tools to search the entire active directory.
! Storage for Application Data
Active Directory Domain Service provides a central location to store data that is shared between applications, and with applications that need to distribute their data across entire windows networks.
! Efficient Synchronization of directory updates
Updates are distributed throughout the network through secure and cost-efficient replication between domain controllers.
! Remote Administration
It is possible, providing the user has been granted appropriate permissions, to connect to any domain controllers remotely from any windows based computer that has windows server administrative tools installed.
! Single, modifiable, and extensible schema
The schema is the definition of the objects and their attributes that can be created in Active Directory Domain Service. It is possible to modify the schema to create new attributes that can be used to implement new types of objects or to extend existing objects. For example, attributes of the user object store information, such as user name, password, and telephone number.
! Integration of service names with DNS, The internet standard name resolution service
Active Directory Domain Service relies on DNS to implement an IP-based naming system so that the active directory domain controllers are locatable over standard IP, both on Intranet and Internet.
! Light Weight Directory Access protocol (LDAP) Support
Light Wight Directory Access Protocol is the industry standard directory access protocol, making AD DS widely accessible to management and query applications. Active Directory Domain Services support LDAP version 2 and LDAP version 3.
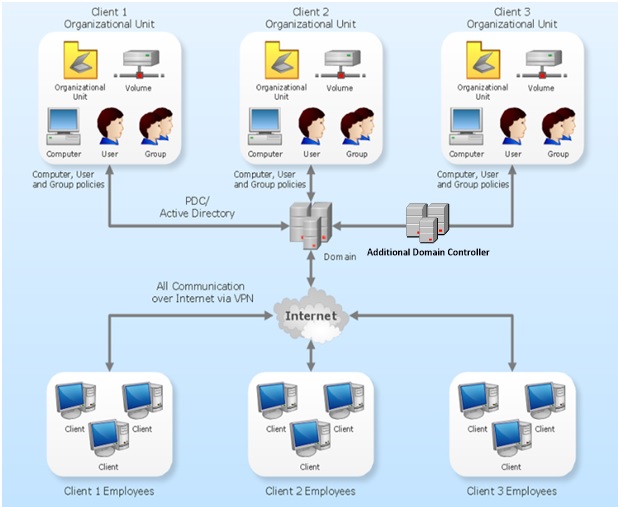
Over view of Network Diagram:
In your organization datacenter we will configure three domain controller for your network. And if there is any situation raised to configure more servers in your premises, we will do it accordingly.
Forest:
At its highest level, a forest is a single instance of Active Directory. Therefore, a forest is synonymous with Active Directory, meaning that the set of all directory partitions in a particular Active Directory instance (which includes all domain, configuration, schema and optional application information) makes up a forest. This means that when you have multiple forests in an enterprise they will, by default, act separately from each other as if they were the only directory service in your organization.
This behavior, however, is easily be modified so that multiple forests can share Active Directory responsibilities across an enterprise. This is done by creating external or forest trust relationships between the forests. In this way, each forest can be connected with every other forest to form a collaborative directory service solution for any enterprise with business needs that include multiple forest collaboration.
Domain Controller:
A domain controller is a server that is running a version of the Windows Server® operating system and has Active Directory® Domain Services installed. By default, a domain controller stores one domain directory partition consisting of information about the domain in which it is located, plus the schema and configuration directory partitions for the entire forest. A domain controller that runs Windows Server 2012, 2012 R2, 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server 2003 can also store one or more application directory partitions. There are also specialized domain controller roles that perform specific functions in an AD DS environment. These specialized roles include global catalog servers and operations masters.
Global Catalog Servers:
Every domain controller stores the objects for the domain in which it is installed. However, a domain controller designated as a global catalog server stores the objects from all domains in the forest. For each object that is not in the domain for which the global catalog server is authoritative as a domain controller, a limited set of attributes is stored in a partial replica of the domain. Therefore, a global catalog server stores, own full writable domain replica (all objects and all attributes) plus a partial, read-only replica of every other domain in the forest. The global catalog is built and updated automatically by the AD DS replication system. The object attributes that are replicated to global catalog servers are the attributes that are most likely to be used to search for the object in AD DS. The attributes that are replicated to the global catalog are identified in the schema as the partial attribute set (PAS) and are defined by default by Microsoft. However, to optimize searching, you can edit the schema by adding or removing attributes that are stored in the global catalog.
The global catalog makes it possible for clients to search AD DS without having to be referred from server to server until a domain controller that has the domain directory partition storing the requested object is found. By default, AD DS searches are directed to global catalog servers.
The first domain controller in a forest is automatically created as a global catalog server. Thereafter, you can designate other domain controllers to be global catalog servers if they are needed.
Operation Master:
Domain controllers that hold operations master roles are designated to perform specific tasks to ensure consistency and to eliminate the potential for conflicting entries in the Active Directory database. AD DS defines five operations master roles: the schema master, domain naming master, relative identifier (RID) master, primary domain controller (PDC) emulator, and infrastructure master.
The following operations masters perform operations that must occur on only one domain controller in the forest:
Schema master
Domain naming master
The following operations masters perform operations that must occur on only one domain controller in a domain:
Primary Domain Controller (PDC) emulator
Infrastructure master
Relative ID (RID) master
Brief description of Active Directory FSMO Roles in Windows Server 2008 R2/ 2012 R2:
Schema Master: There can only be one Schema Master defined per forest. The Schema Master contains the only writable copy of the schema and additions to it can only be done by a member of the Schema Admins and the Enterprise Admins security group. When this role is unavailable additions or changes to the schema cannot be made.
Domain Naming Master: The Domain Naming Master is responsible for the addition or removal of domains in the forest. The Domain Naming Master is a forest-wide role, which means only one can be defined per forest. When this role is unavailable no domains can be added, removed or renamed.
Infrastructure Master:The Infrastructure Master is a domain-wide role, which means it is defined per domain. Logically, if you have 3 domains within your forest, you have 3 domain controllers that contain the Infrastructure Master role. The Infrastructure Master is responsible for updating links to objects in the domain to objects in other domains. There can only be one defined per-domain. When the infrastructure master is unavailable changes in objects do not get replicated. However, when all domain controllers are also a Global Catalog, the Infrastructure Master does not have a function.
RID Master: The RID (or Relative-ID) Master is responsible for RID-requests from all domain controllers within that domain. When the RID pool of a domain controller depletes, it requests a new pool from the RID Master. The RID Master can only be defined once per domain. When the RID Master is unavailable and a domain controller runs out of available RID's no new objects (as users, groups, computers and such) cannot be created.
PDC Emulator: The PDC (or Primary Domain Controller) Emulator role is used to act as PDC when Windows NT BDC's are used. The PDC Emulator also acts as Master Browser for the domain and handles password updates for the domain. The PDC Emulator can only be defined once per domain. When the PDC Emulator is unavailable password-changes get updated with the regular replication traffic instead of right away through the PDC emulator. Also, the time (net time) will not get synced during this time, which can be an issue in a domain environment.
Additional Domain Controller: We will install and configure additional domain controllers to the domain to improve the availability and reliability of network services. Adding additional domain controllers can help provide fault tolerance, balance the load of existing domain controllers, and provide additional infrastructure support to sites.
More than one domain controller in a domain makes it possible for the domain to continue to function if a domain controller fails or must be disconnected. Multiple domain controllers can also improve performance by making it easier for clients to connect to a domain controller when logging on to the network.
Group Policy Management: A strategically designed Active Directory Group helps simplify administration & achieve maximum flexibility. However configuring groups and assigning various group attributes is a complex procedure that involves numerous steps using native Active Directory tools. Group Policy will full fill your most of the compliance requirements.
Group policy will provide you flexibility for managing below policy:
➢ Bulk User Management
➢ Password Management
➢ Application Locker Management
➢ Banner MOTD Management
➢ Advanced Firewall and Security Management
➢ Account Lockout Policy Management
➢ File Synchronization Management
➢ Contact Management
➢ Delegation Management
➢ USB devices Management
➢ Remote Share Administration and Sharing Security
➢ Unused Port Blocking by using Security Configuration
➢ Department Wise organizational unit and security policy
➢ Audit Policy
➢ User Rights Assignments
➢ Security Options
➢ System Services
➢ Join us on:
➢ http://www.facebook.com/cnspbd